Common Name: Pomegranate
Botanical name: Punica granatum
Summary
A shrubby tree that is deciduous in cooler climates, and evergreen in warmer climates, with large edible and highly ornamental fruits, growing to 5m high and as wide.
Originating from Iran and Afghanistan in ancient times, today the pomegranate is grown from the tropics to very cold climates and is favoured in the Mediterranean diet. Extremely drought tolerant, yet watering will greatly improve fruit yield.
Grown as a single trunk with four or five main branches. Pruning of vigorous growth will keep the tree tidy.
Likes
- Cool winters
- Very hot and dry summers
- Most soil types
Doesn’t like
- Cool summers (poor fruit size)
Flowers in
Spring – Summer
Fruits in
Late Autumn
Care
Planting
Plant the dormant tree in full sun.
Pollination
Self-fertile, requires another tree to increase yields but is not required.
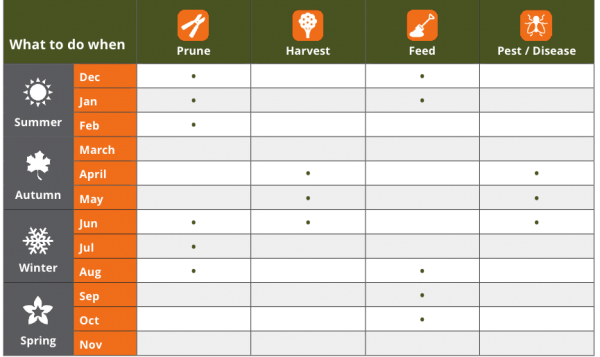
Pruning
Pomegranates sucker profusely, remove all suckers continually. Fruit on short spurs or shoots at the end of branches for 3-4 years. Shorten to renew fruiting wood. Cut untidy and leggy growth. Winter and summer.
Disease and pest management
The fruit is susceptible to fungal rot.
Moisture
Maintain water from flowering to fruit, reduce watering as fruits ripen.
Feeding
Low feeder, high nitrogen NPK fertiliser if growth is inadequate.
Harvesting
Pick fruit in late autumn before heavy rain which will split fruit. Be gentle as the fruit will bruise easily. Fruit will store for a month or two.